What is statistical inference?
Statistical inference is the process of drawing conclusions about the underlying truth based on the evidence. It involves estimating parameters, testing hypotheses, and quantifying uncertainty. This process relies on probability theory and computational methods to derive meaningful insights from data.
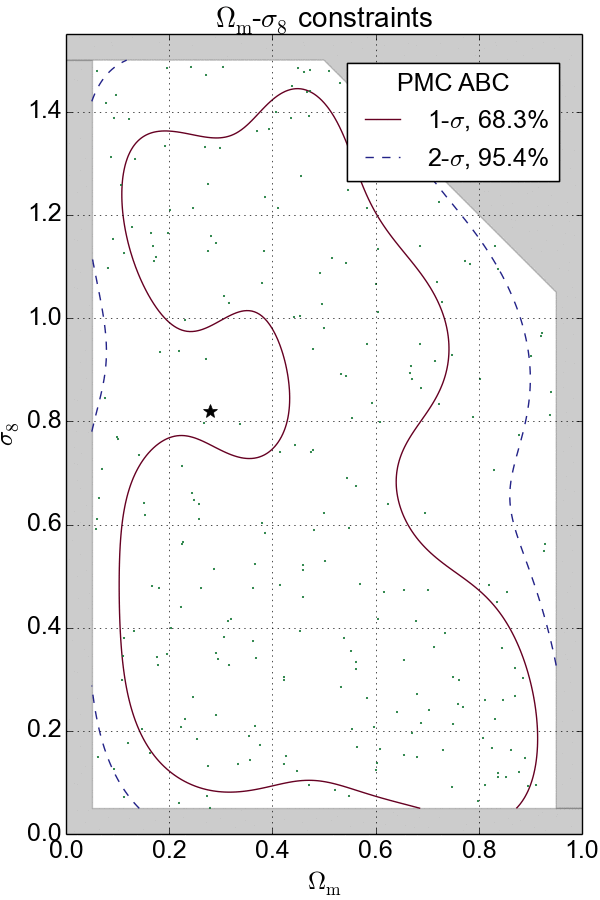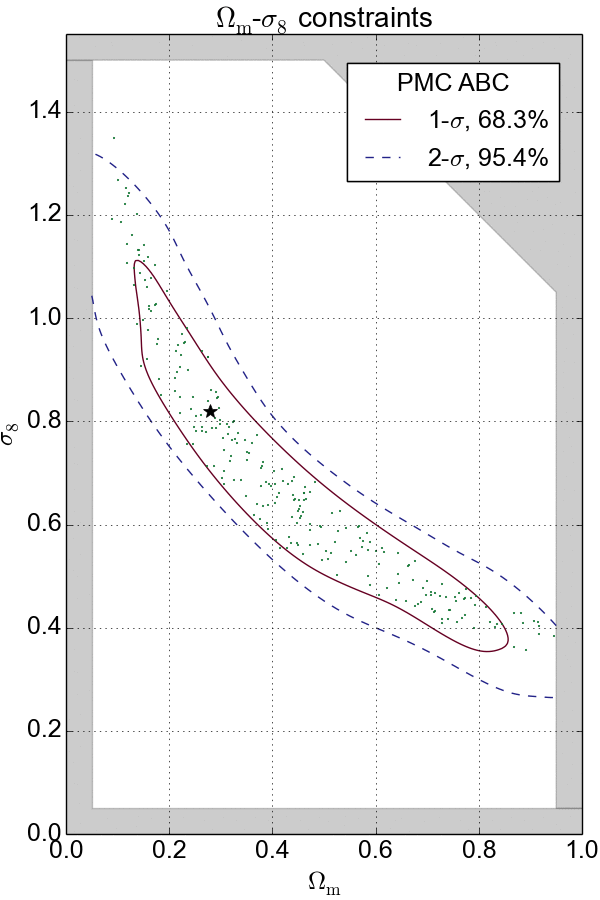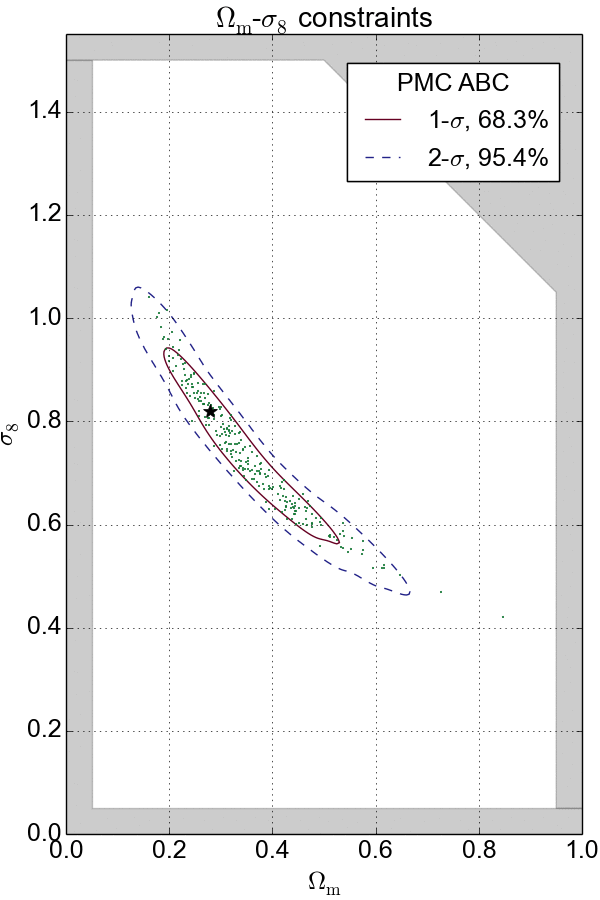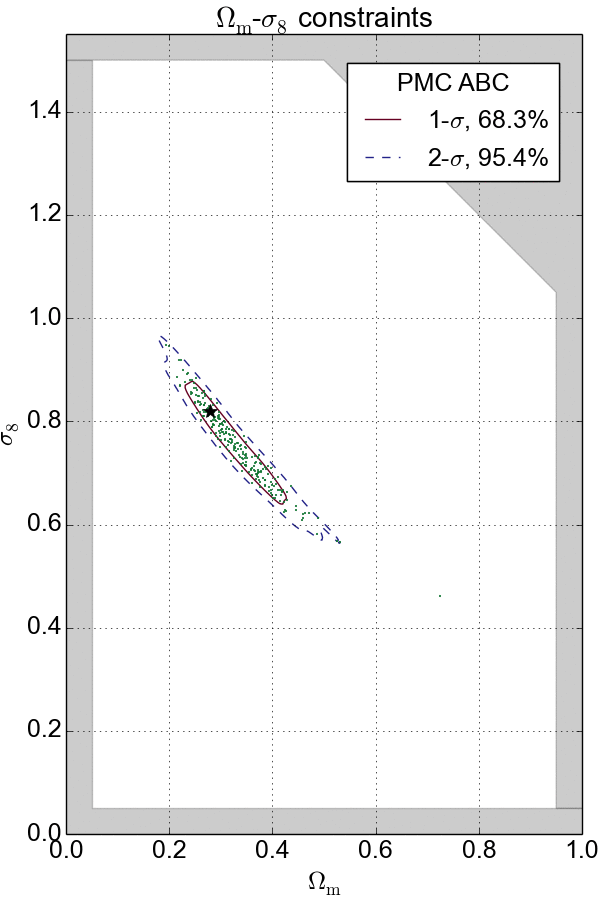
In my past experience, I have extensively applied Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) and Population Monte Carlo (PMC) as sampling technique to navigate and probe the density of complex distributions in high-dimensional spaces.
Intractable likelihood
In the cases where the likelihood function is intractable, likelihood-free inference techniques such as Approximate Bayesian Computation (ABC) and Variational Inference (VI) are used to provide efficient approximations to posterior distributions. These techniques have been successfully applied in my cosmological analyses.